Digital Literacy and Civic Engagement

Explore the power of digital literacy in fostering inclusion and engagement in education at our upcoming joint webinar series. This session brings together two experts sharing insights from diverse educational contexts.
Presentation 1: Dr. Tati Lathipatud Durriyah, from Universitas Islam Internasional Indonesia (UIII), will present her preliminary findings on digital literacy in high schools across Jabodetabek (Greater Jakarta) area. Her research examines teachers’ experiences with digital tools, uncovering both the transformative potential of digital literacy and significant challenges, such as resource limitations and adapting teaching methods. Her findings offer a candid look at the journey toward digital integration in Indonesian classrooms.
Presentation 2: Dr. Emily H. White, Lecturer in Learning Intervention at the University of Melbourne, presents her research on digital literacy development for students with intellectual disabilities and Autism. Dr. White’s work highlights how structured teaching strategies and assessment tools empower students with disabilities to engage with digital technologies. Her research demonstrates how digital literacy can foster greater inclusion and open pathways to lifelong learning.
Join us to gain actionable insights into advancing digital literacy for civic engagement and inclusive education.
Mark your calender on:
?Day/Date: Tuesday, November 19, 2024
⏰Time: 13.00-14.00 (JKT Time) / 17.00-18.00 (Melbourne Time)
Registration: bit.ly/JointWebinarSeries2
E-Certificate is provided!
Recorded on YouTube
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6cNq6L1mzOU&list=PLX82ye7O55cfcRgvsXb1M1hRQIr6sjnwz
Guest Lecture: INDONESIA’S PHILOSOPHY OF PANCASILA: The Challenges for The Youth amidst Cultural Shift and Globalization

?Guest Lecture:
INDONESIA’S PHILOSOPHY OF PANCASILA: The Challenges for The Youth amidst Cultural Shift and Globalization
speaker:
Prof. Dr. M. Amin Abdullah
Professor of Islamic Philosophy
Universitas Islam Negeri Sunan Kalijaga
moderator:
R. Alpha Amirrachman, MPhil, PhD
Faculty of Education
Universitas Islam Internasional Indonesia
? Monday, Nov 18, 2024
⏰ 09.00-11.30 a.m. Jakarta Time
? Teleconference Room,
2nd Floor
Faculty of Education, UIII
or via Zoom:
? bit.ly/GuestLecture_Equity
The rapid pace of globalization and the cultural shifts have brought unprecedented challenges to the values embedded in Indonesia’s philosophy of Pancasila. The Indonesian youth are exposed to global cultures through media and technology, which could be inline or conflict with the local ethos and the principles of Pancasila of believe in God, humanity, unity, democracy and social justice. This exposure can lead to a dilution of national identity as young Indonesians navigate between global, national and local values.
Distinguished philosopher Prof Amin Abdullah will critically break down and contextualize Pancasila’s principles and review the operationalization of pluralism and respect for diversity to also see if everyone has equal access to quality education. Prof Amin will likewise explore the opportunities as Indonesian youth interact with their peers around the globe.
Please come to our campus to interact directly with Prof Amin or you can also join the discussion via Zoom.
Open for public.
E-certificate is provided.
Faculty of Education
Universitas Islam Internasional Indonesia (UIII)
??
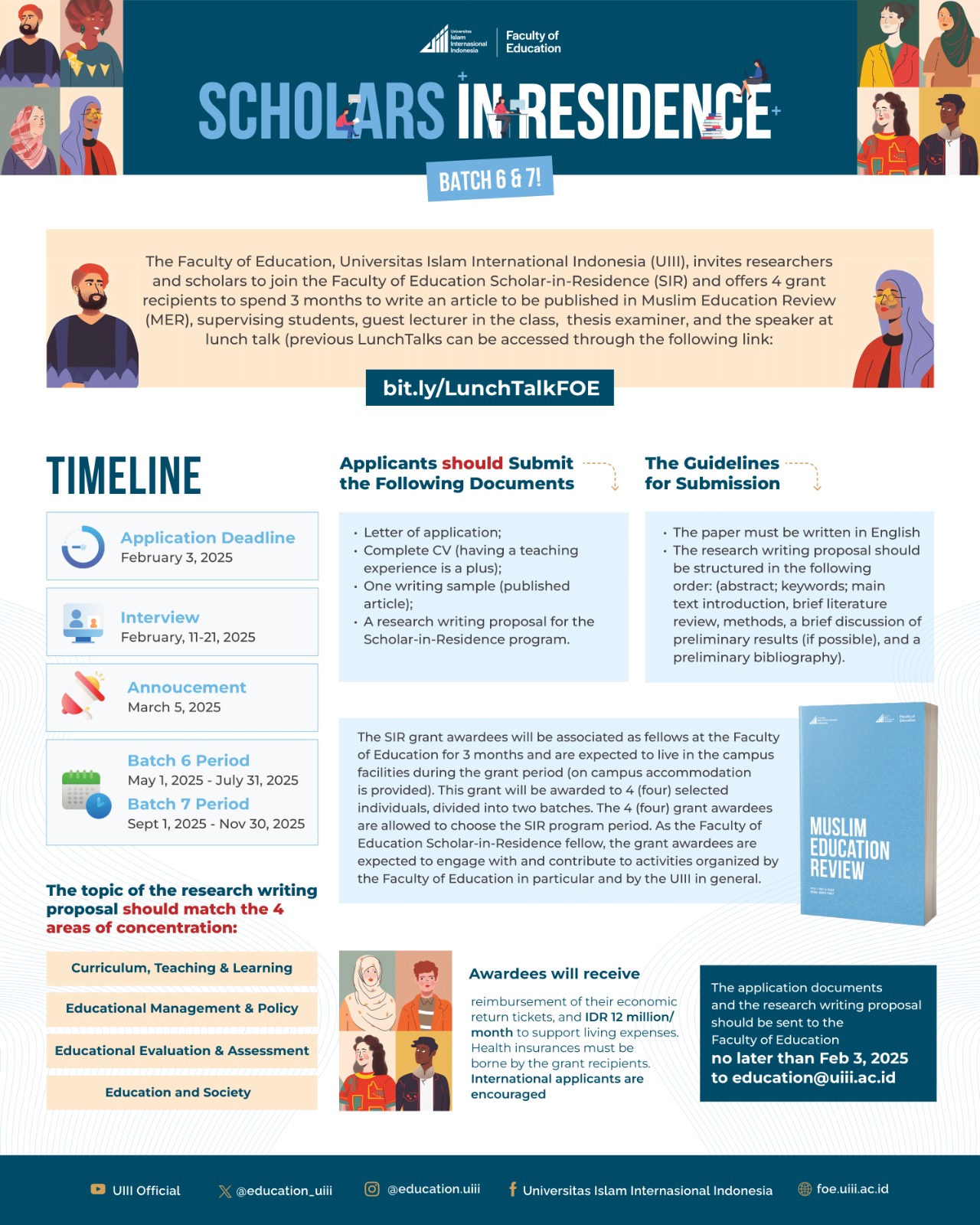
Scholars in Residence 2025 Batch 6 & 7

The Faculty of Education at UIII invites all Ph.D. holders to participate in the Scholar-in-Residence (SIR) Program 2025, Batch 6 & 7 to spend three months as a research fellow.
During the grant period, awardees are expected to serve as guest lecturers, provide academic consultations, act as thesis examiners, present at a LunchTalk, and publish an article in Muslim Education Review (MER). The topic of the article should match the four areas of concentration at the Faculty of Education:
➡Curriculum, Teaching, & Learning
➡Educational Management & Policy
➡Educational Evaluation and Assessment
➡Education and Society
Each recipient will receive IDR 12 Million per month (excluding tax) and are expected to live in the campus facilities during the grant period (reimbursement of economic return tickets and on-campus accommodation are provided).
The awardees will start on:
➡May 1 – July 31, 2025 (Batch 6)
➡September 1 – November 30, 2025 (Batch 7)
Requirements:
➡CV
➡Application Letter
➡Writing sample (published article)
➡Research writing proposal (to be published in MER)
?Deadline: February 3, 2025
?Send your application to: education@uiii.ac.id
Please make sure to read all the details about the program.
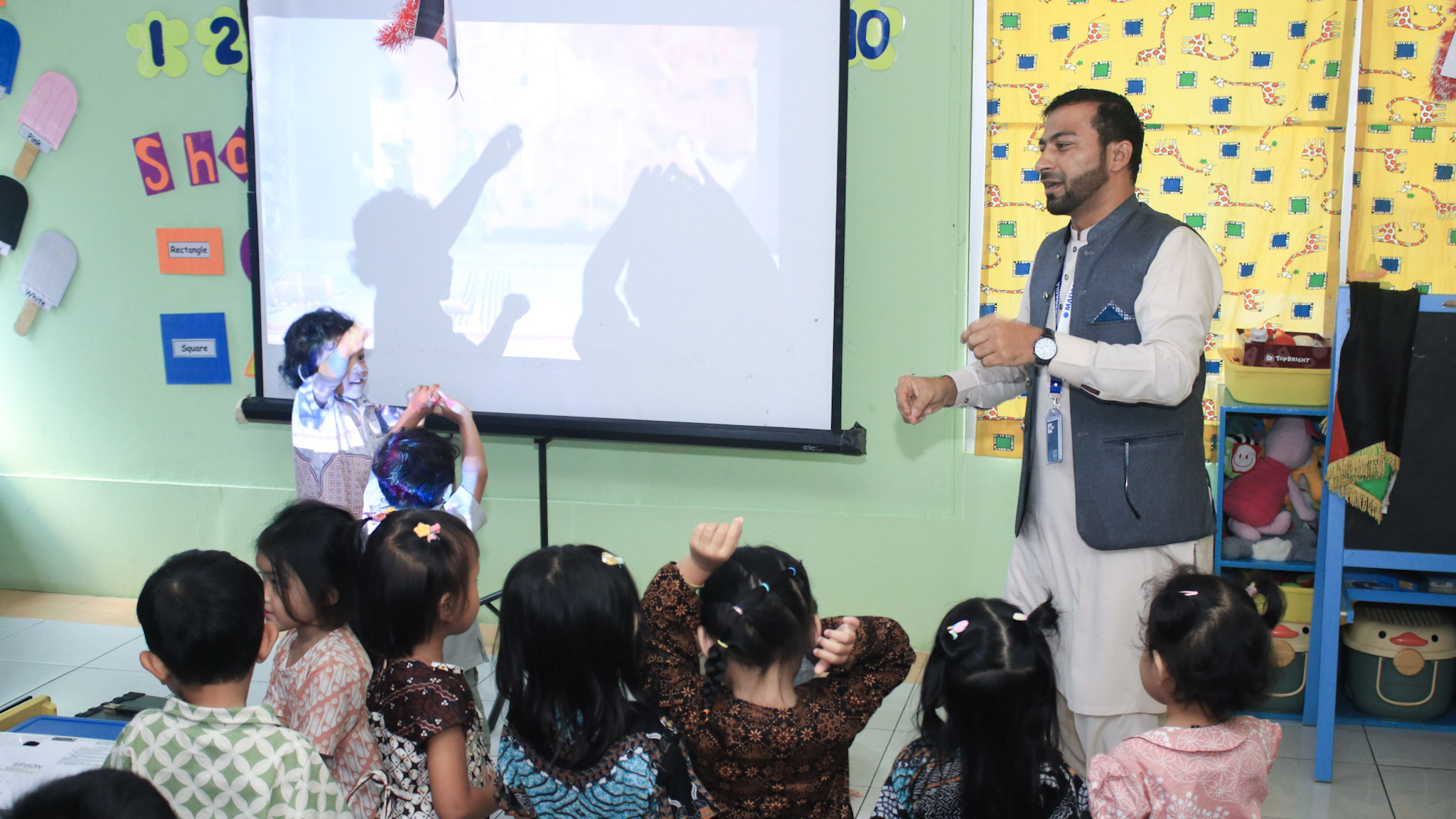
An Inspiring Journey at Madania Progressive Indonesian School
 An Inspiring Journey at Madania Progressive Indonesian School
An Inspiring Journey at Madania Progressive Indonesian School
By Khizer Hayat.
As an intern, I practiced my skills in teaching English there. Madania, a school known for its progressive approach to education, integrates the Indonesian National Curriculum with the International Baccalaureate (IB) and Cambridge IGCSE frameworks, creating an exceptional learning environment from Kindergarten through Senior High School. Teaching English here was an incredibly rewarding experience. I had the unique opportunity to engage with a wide age group of students, adapting my lessons to their varied needs while ensuring their grasp of English communication improved.
One of the highlights of my experience was how I was able to bridge cultures through language. I was not just an English teacher, but also a cultural ambassador, fostering intercultural connections during my time with the students. Participating in school-wide events such as the Indonesian Independence Day, Mawlid Nabi(Prophet Muhammad’s Birthday Celebration), and cultural celebrations provided a platform to engage with parents and the wider school community. These moments allowed me to share my background while appreciating the rich cultural diversity Indonesia offers.
Working with students wasn’t limited to classrooms alone. Madania emphasizes holistic development, blending academics with extracurricular activities like sports and arts, which provide an avenue to engage with students on multiple levels. The school’s focus on inclusivity and promoting a diverse understanding of religion, languages, and cultures resonated deeply with me. I experienced this openness firsthand when the school management and staff generously invited me on visits to significant places in Bogor. Their hospitality was heartwarming, reinforcing the values of unity and respect for diversity that Madania upholds.
My time at Madania wasn't just about teaching—it was about learning. I gained hands-on exposure to various teaching and management practices. I contributed to the evaluation of the curricula, observed the implementation of progressive teaching methods, and participated in policy discussions aimed at strengthening the school’s educational approach. I was impressed by the school’s openness to feedback, where I functioned not only as a teacher but also as a critical observer, offering suggestions on curriculum alignment and educational research.
Madania’s commitment to nurturing future leaders—through modern technology, cultural understanding, and academic excellence—stood out. The school’s holistic approach made it a unique institution within Indonesia. I left with a deeper understanding of how education can be a force for both personal and societal growth.
In conclusion, my internship at Madania was more than an academic endeavor; it was an enriching experience that allowed me to grow as a teacher, observer, and participant in a dynamic and diverse educational setting. It reinforced my belief that schools like Madania are shaping the future leaders of Indonesia—leaders who are not only well-versed in academic excellence but are also rooted in cultural and social understanding. I am proud to have carried the name of UIII and contributed to this incredible institution during my time there.
Khizer Hayat is a master student at the Faculty of Education, UIII.
Breaking the Boundaries as an Internship Student: My Journey to Present at a Southeast Asian International Forum
 Breaking the Boundaries as an Internship Student: My Journey to Present at a Southeast Asian International Forum
Breaking the Boundaries as an Internship Student: My Journey to Present at a Southeast Asian International Forum
By Muhammad Lutfi Assidiqi
Attending the Consultative Meeting on Development of SEAMEO-ASEAN Joint Roadmap on Early Childhood Care and Education in Southeast Asia and Policy Brief on Early Childhood Development Services as a presenter, especially to present the draft policy brief that my team and I worked on during our time as interns at SEAMEO CECCEP, was a very valuable and rare experience for an intern. In this meeting, I stood in front of Governing Board (GB) members of Southeast Asian countries as well as representatives of international NGOs such as UNICEF EAPRO, Tanoto Foundation, UNESCO Indonesia, and others. This was not just a presentation, but a pivotal moment in my career where my voice was heard in prestigious forums.
As an intern, I realized that this kind of opportunity is rare. The stereotype of interns as "beginners" who only carry out small tasks, I do not feel at all at SEAMEO CECCEP. Instead of being ignored, my ideas are heard and appreciated, as if I were an integral part of a professional team. This experience encouraged me to continue to explore the material that I had learned from Dr. Lukman in the Education Policy Analysis class. The practice of writing policy briefs based on The Eightfold Path from Bardach that I learned during the lectures proved to be an important provision in completing my job at SEAMEO CECCEP.
I feel very lucky and grateful to the Faculty of Education, UIII, for facilitating the Independent Study Program and matching me with a very supportive internship place. An internship at SEAMEO CECCEP has not only provided me with significant professional experience, but also a space that has supported my personal and academic development. This opportunity has opened my eyes to the importance of an education that connects theory with real practice, and the important of having an environment that supports and rewards every contribution, regardless of status.
By this experience, I reflected on how important and invaluable this kind of opportunity is for a college student. Not only provide real experience in the field of education policy, but also build confidence to contribute in the international level. Of course, with the willingness to keep learning and the desire to keep trying to have a positive impact, as my team and I have done by drafting a policy brief on early childhood development services for the Southeast Asian region.
Estudia: Quirkos Workshop

? Join Us for a Quirkos Workshop with Dr. Bambang Sumintono!
Want to enhance your qualitative data analysis skills? ?
Don’t miss this opportunity to learn how to effectively use Quirkos!
? Date: Tuesday, November 12, 2024
⏰ Time: 9:00 AM – 3:00 PM (with a 1-hour break)
? Location: Faculty A Classroom 10
What is Quirkos??
Quirkos is a user-friendly tool that simplifies qualitative research. It allows researchers to visually organize, code, and analyze textual data, making it easier to uncover patterns and insights.
The workshop will be facilitated by Dr. Bambang Sumintono, a researcher and lecturer, and will guide us through the core features of Quirkos to enhance our research process theoretically and practically ?
Why Attend? ?
? Understand the theoretical and practical things about Quirkos.
? Perform qualitative data analysis with Quirkos.
? Learn from an expert in the field.
? Hands-on experience with Quirkos tools.
Don't miss out on this valuable learning experience, exclusive for FoE students.
Registation link:
https://bit.ly/quirkosworkshopregistration
Register now!
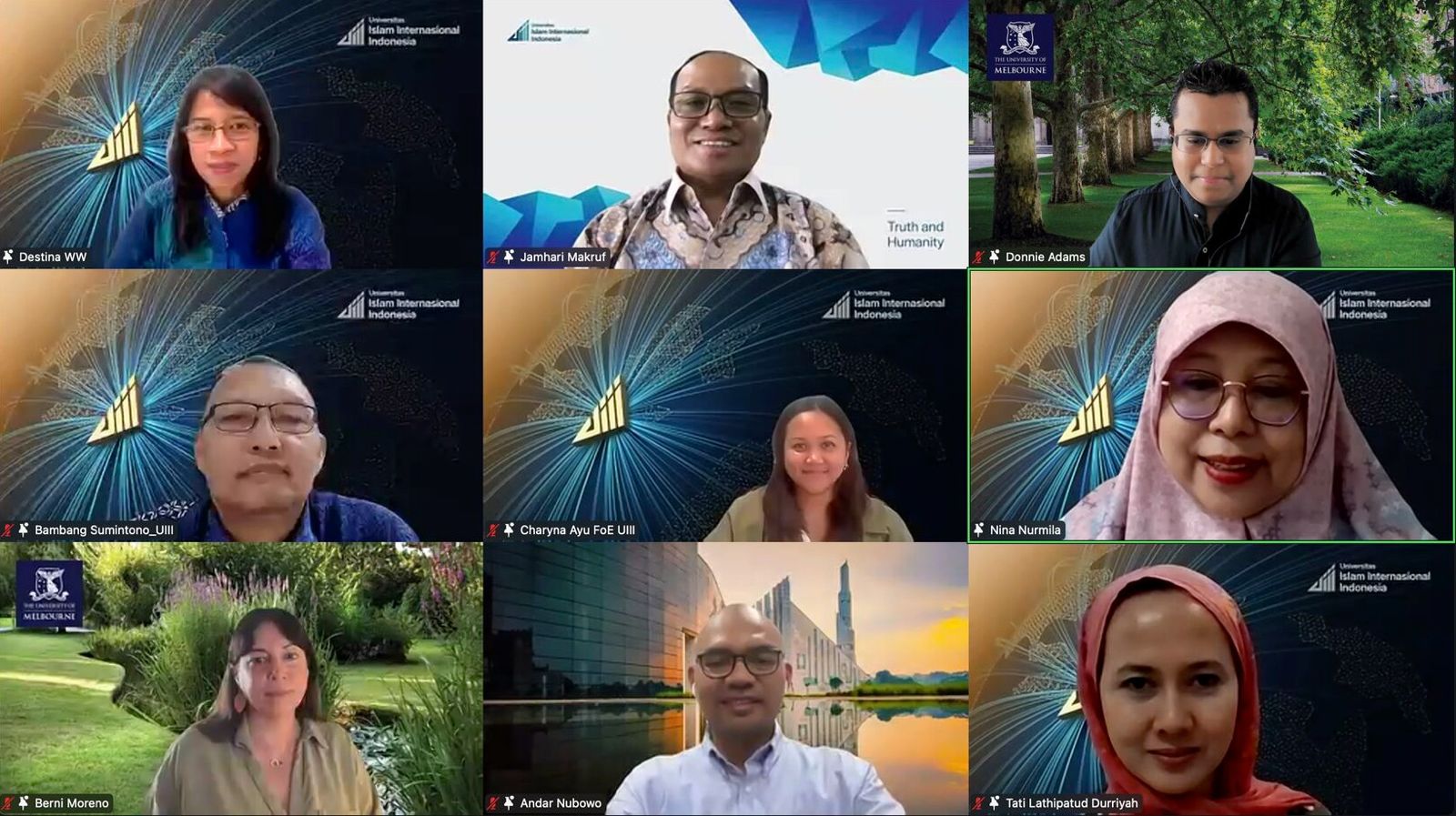
UIII and University of Melbourne Host Joint Webinar on Middle Leadership in Schools

UIII and University of Melbourne Host Joint Webinar on Middle Leadership in Schools
October 18, 2024
Contributor: Supriyono | Editor: Dadi Darmadi
The UIII Faculty of Education and the University of Melbourne, Australia, held a collaborative webinar on Tuesday, October 15, 2024, exploring the essential role of middle leaders in Malaysian and Indonesian schools. The event, themed “The Role of Middle Leaders in Malaysian and Indonesian Schools,” attracted educational practitioners and researchers interested in leadership dynamics in the Southeast Asian context.
Dr. Bambang Sumintono, a lecturer and Head of the PhD in Education program at UIII, opened the discussion with his presentation titled “Bridging the Gap: Understanding the Role of Middle School Leaders in Indonesia’s Educational System,” sharing findings from his ongoing UIII-funded research.
Dr. Sumintono highlighted a unique aspect of Indonesian middle school leadership, saying that middle leaders are often appointed either by popular vote from their peers or through direct appointment by school principals. This approach creates a distinct dynamic, though also provides potential drawbacks as the appointed might not properly prepare for filling up the position.
The second speaker, Dr. Donnie Adams, a lecturer at the Faculty of Education, the University of Melbourne, delivered his presentation titled “Shaping Futures: Middle Leadership Roles in Malaysian Schools.” Focusing on Malaysia’s multi-ethnic school system, Dr. Adams discussed the role of middle leaders in national schools, Tamil schools, and Chinese schools, each with its own unique cultural context.
Compared to Indonesia, the dynamic of school leaders in Malaysia, as presented by Dr. Adams, emphasized a more structured process, dynamized by the multicultural aspects each school has either from Malay national influence, or Chinese and Tamil cultures. This highlighted that context is crucial in shaping middle leadership practices.
The webinar concluded with an engaging Q&A session, where participants delved deeper into the roles of middle leaders within Indonesian and Malaysian educational systems. The event underscored the importance of middle leaders in building adaptive, culturally aware schools and highlighted areas for potential cross-cultural research and collaboration.
Both UIII and the University of Melbourne expressed optimism about further joint initiatives to deepen understanding and strengthen educational leadership across Southeast Asia. Both parties are committed to continuing their collaboration in holding the next series of webinars in the future.
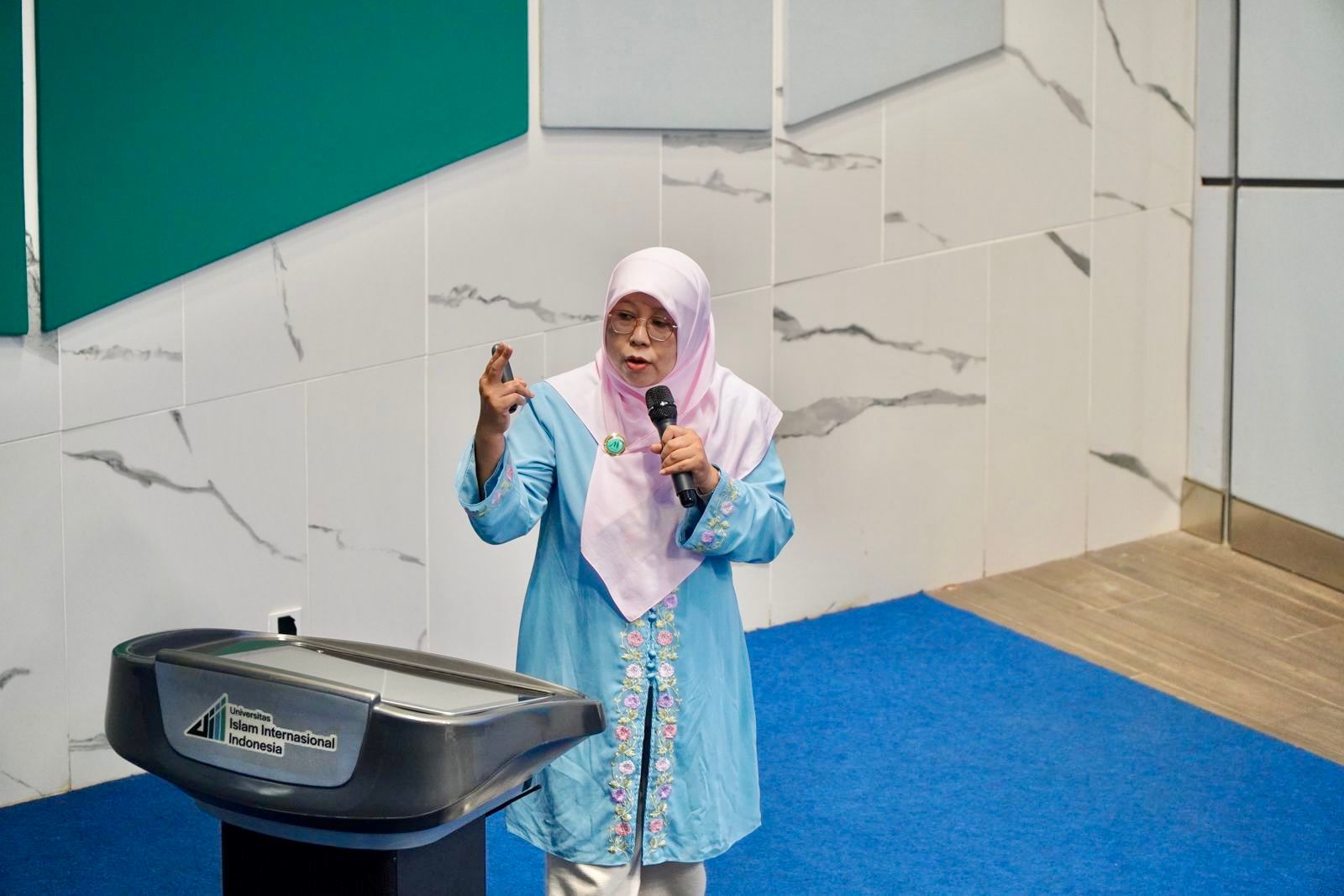
A Deeper Understanding of Critical Feminist Methodology
A Deeper Understanding of Critical Feminist Methodology
October 14, 2024
Contributor: Supriyono | Editor: Dadi Darmadi | Photo: M. Sufyan As-Tsauri
Depok, October 3, 2024 — The UIII Faculty of Education held a thought-provoking public lecture on Thursday, October 3, featuring Prof. Nina Nurmila, Dean of the Faculty of Education. Speaking to a packed audience in Theater Hall Faculty A, Prof. Nurmila explored the intricacies of critical feminist methodology, a vital yet often debated aspect of modern research.
Prof. Nina Nurmila is a distinguished Professor of Gender and Islamic Studies. She earned her MA from Murdoch University in 1997 and a PhD from the University of Melbourne in 2007. Her academic journey includes prestigious roles such as a Fulbright Visiting Researcher at Temple University in Philadelphia in 2000, an Endeavour Postdoctoral Research Fellow at the University of Technology, Sydney, in 2008, and a Fulbright Visiting Professor of Islamic Studies at the University of Redlands, California, from 2008 to 2009.
Prof. Nurmila began by addressing ongoing debates from the 1990s over whether feminist methodology stands as a distinct research paradigm and methodology. She pointed out that opponents have argued against its independence, suggesting that feminist methodologies lack a unique perspective and draw heavily from established paradigms like Marxism and critical theory. Others contend that feminist approaches lack coherence due to the diverse perspectives within feminism itself.
However, Prof. Nurmila presented a compelling case for recognizing feminist methodology as unique, emphasizing its intentional rejection of male-dominated research paradigms. “Feminist researchers prioritize women’s perspectives and their societal positions, presenting a contrast to traditional methodologies focused primarily on male experiences,” she explained. She further noted that feminist research introduces a unique lens for understanding the world, often centered around the impact of patriarchy.
The criteria that define feminist methodology, as presented by Prof. Nurmila, include examining issues through a female prism, in which women are both the focus and interpreters of inquiry. Feminist methodology also encourages “consciousness raising,” a quality described as the advantage that female researchers have in understanding women’s experiences from within an “oppressed group.” She added that this “double vision” enables feminist researchers to empathize deeply and interpret their findings more accurately.
Highlighting her own work, Prof. Nurmila referenced several examples of feminist research, including her publications like “Women, Islam, and Everyday Life” (Routledge, 2009) and an article examining husband-wife dynamics (Al-Jamia’ah: Journal of Islamic Studies, 2013). She reflected on how feminist methodology shapes her qualitative research, occasionally integrating quantitative data while retaining a feminist analytical lens.
In her conclusion, Prof. Nurmila discussed how feminist methodologies transform traditional academic language structures, shifting from objective, passive language to more subjective, active voice. She also emphasized the importance of non-gender-biased language, advocating for inclusive terms such as “human power” rather than “manpower”.
Prof. Nurmila’s lecture left the audience with a deeper understanding of critical feminist methodology and its transformative impact on research. Through her insights, she highlighted the importance of inclusivity and empowerment within academia, calling on future researchers to consider feminist perspectives in fostering societal progress. The event exemplified UIII’s commitment to fostering an environment open to new perspectives in research, welcoming research paradigms, methodologies, and methods that advocate for societal change and scholarly diversity.
source: https://uiii.ac.id/events/read/57698/a-deeper-understanding-of-critical-feminist-methodology