UIII and University of Melbourne Host Joint Webinar on Middle Leadership in Schools

UIII and University of Melbourne Host Joint Webinar on Middle Leadership in Schools
October 18, 2024
Contributor: Supriyono | Editor: Dadi Darmadi
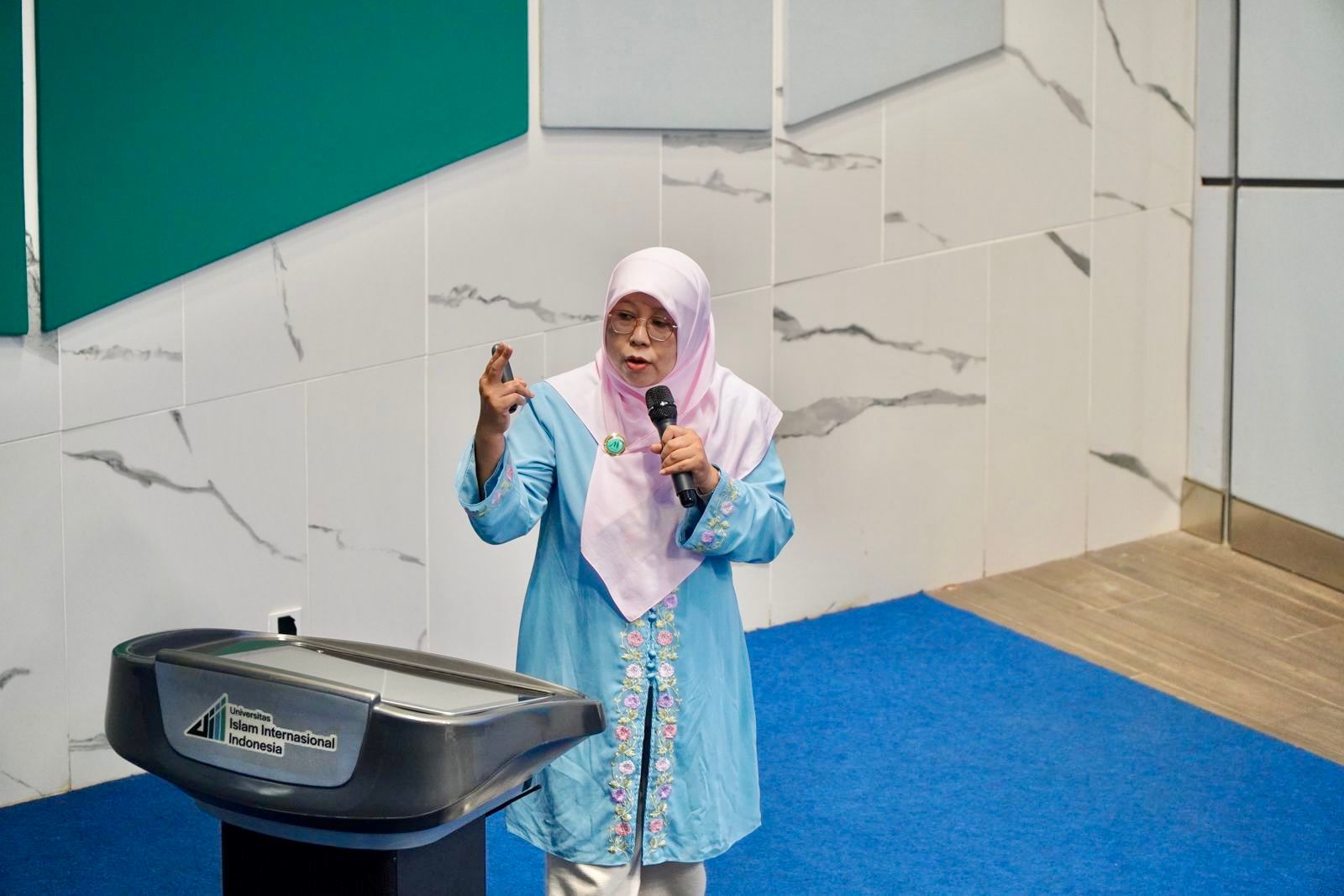
The UIII Faculty of Education and the University of Melbourne, Australia, held a collaborative webinar on Tuesday, October 15, 2024, exploring the essential role of middle leaders in Malaysian and Indonesian schools. The event, themed “The Role of Middle Leaders in Malaysian and Indonesian Schools,” attracted educational practitioners and researchers interested in leadership dynamics in the Southeast Asian context.
Dr. Bambang Sumintono, a lecturer and Head of the PhD in Education program at UIII, opened the discussion with his presentation titled “Bridging the Gap: Understanding the Role of Middle School Leaders in Indonesia’s Educational System,” sharing findings from his ongoing UIII-funded research.
Dr. Sumintono highlighted a unique aspect of Indonesian middle school leadership, saying that middle leaders are often appointed either by popular vote from their peers or through direct appointment by school principals. This approach creates a distinct dynamic, though also provides potential drawbacks as the appointed might not properly prepare for filling up the position.
The second speaker, Dr. Donnie Adams, a lecturer at the Faculty of Education, the University of Melbourne, delivered his presentation titled “Shaping Futures: Middle Leadership Roles in Malaysian Schools.” Focusing on Malaysia’s multi-ethnic school system, Dr. Adams discussed the role of middle leaders in national schools, Tamil schools, and Chinese schools, each with its own unique cultural context.
Compared to Indonesia, the dynamic of school leaders in Malaysia, as presented by Dr. Adams, emphasized a more structured process, dynamized by the multicultural aspects each school has either from Malay national influence, or Chinese and Tamil cultures. This highlighted that context is crucial in shaping middle leadership practices.
The webinar concluded with an engaging Q&A session, where participants delved deeper into the roles of middle leaders within Indonesian and Malaysian educational systems. The event underscored the importance of middle leaders in building adaptive, culturally aware schools and highlighted areas for potential cross-cultural research and collaboration.
Both UIII and the University of Melbourne expressed optimism about further joint initiatives to deepen understanding and strengthen educational leadership across Southeast Asia. Both parties are committed to continuing their collaboration in holding the next series of webinars in the future.
A Deeper Understanding of Critical Feminist Methodology
A Deeper Understanding of Critical Feminist Methodology
October 14, 2024
Contributor: Supriyono | Editor: Dadi Darmadi | Photo: M. Sufyan As-Tsauri
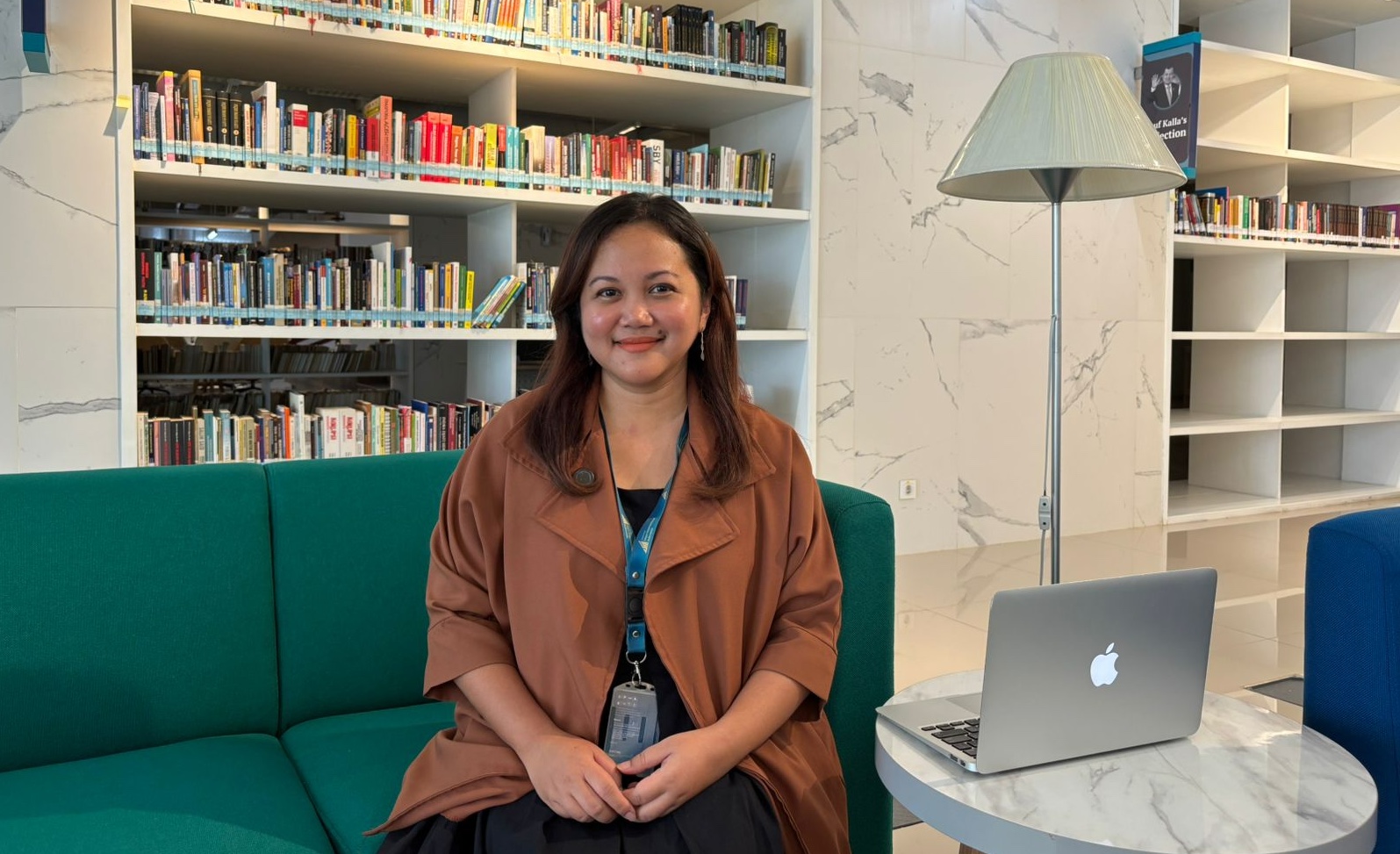
Depok, October 3, 2024 — The UIII Faculty of Education held a thought-provoking public lecture on Thursday, October 3, featuring Prof. Nina Nurmila, Dean of the Faculty of Education. Speaking to a packed audience in Theater Hall Faculty A, Prof. Nurmila explored the intricacies of critical feminist methodology, a vital yet often debated aspect of modern research.
Prof. Nina Nurmila is a distinguished Professor of Gender and Islamic Studies. She earned her MA from Murdoch University in 1997 and a PhD from the University of Melbourne in 2007. Her academic journey includes prestigious roles such as a Fulbright Visiting Researcher at Temple University in Philadelphia in 2000, an Endeavour Postdoctoral Research Fellow at the University of Technology, Sydney, in 2008, and a Fulbright Visiting Professor of Islamic Studies at the University of Redlands, California, from 2008 to 2009.
Prof. Nurmila began by addressing ongoing debates from the 1990s over whether feminist methodology stands as a distinct research paradigm and methodology. She pointed out that opponents have argued against its independence, suggesting that feminist methodologies lack a unique perspective and draw heavily from established paradigms like Marxism and critical theory. Others contend that feminist approaches lack coherence due to the diverse perspectives within feminism itself.
However, Prof. Nurmila presented a compelling case for recognizing feminist methodology as unique, emphasizing its intentional rejection of male-dominated research paradigms. “Feminist researchers prioritize women’s perspectives and their societal positions, presenting a contrast to traditional methodologies focused primarily on male experiences,” she explained. She further noted that feminist research introduces a unique lens for understanding the world, often centered around the impact of patriarchy.
The criteria that define feminist methodology, as presented by Prof. Nurmila, include examining issues through a female prism, in which women are both the focus and interpreters of inquiry. Feminist methodology also encourages “consciousness raising,” a quality described as the advantage that female researchers have in understanding women’s experiences from within an “oppressed group.” She added that this “double vision” enables feminist researchers to empathize deeply and interpret their findings more accurately.
Highlighting her own work, Prof. Nurmila referenced several examples of feminist research, including her publications like “Women, Islam, and Everyday Life” (Routledge, 2009) and an article examining husband-wife dynamics (Al-Jamia’ah: Journal of Islamic Studies, 2013). She reflected on how feminist methodology shapes her qualitative research, occasionally integrating quantitative data while retaining a feminist analytical lens.
In her conclusion, Prof. Nurmila discussed how feminist methodologies transform traditional academic language structures, shifting from objective, passive language to more subjective, active voice. She also emphasized the importance of non-gender-biased language, advocating for inclusive terms such as “human power” rather than “manpower”.
Prof. Nurmila’s lecture left the audience with a deeper understanding of critical feminist methodology and its transformative impact on research. Through her insights, she highlighted the importance of inclusivity and empowerment within academia, calling on future researchers to consider feminist perspectives in fostering societal progress. The event exemplified UIII’s commitment to fostering an environment open to new perspectives in research, welcoming research paradigms, methodologies, and methods that advocate for societal change and scholarly diversity.
source: https://uiii.ac.id/events/read/57698/a-deeper-understanding-of-critical-feminist-methodology
Happy World Mental Health Day from UIII

Happy World Mental Health Day from UIII
October 10, 2024
By A/Prof. Charyna Ayu Rizkyanti, Ph.D*
The recent increase in student suicide cases highlights significant issues within the educational system. These cases may represent the tip of the iceberg of many intricate psychological challenges within the educational setting that have been overlooked and lack effective comprehensive solutions. To be frank, one of the vulnerable populations most likely to experience mental health problems is university students.
In 2023, over three-quarters of college students (76%) experienced moderate to serious psychological distress, with 36% of students diagnosed with anxiety, 31% meeting the criteria for suicidal ideation, and 13% having intentionally injured themselves within the year (American College Health Association, 2023). In Indonesia, it has been reported that mental disorders now often occur in the 18–25-year age group. This phenomenon is closely related to students, including college students, with about 64% of the younger generation experiencing anxiety problems, while 61.5% of them have symptoms of depression (Kemdikbud.go.id, 2023).
Serious mental health issues can affect our relationships, career, and long-term goals, including our studies, such as struggling with academic demands, adjustment issues, and managing various responsibilities. Thus, it is crucial to create a positive, safe, and supportive environment where students do not solely focus on being the best of the best in academic matters, which might lead them to become super competitive and ambitious individuals, and further, narcissistic. On top of that, it is essential to foster students and remind them that each of them is unique with different potential. As a consequence, campuses must rethink their approach (American Psychological Association, 2022). Educational institutions need to provide counseling services on campus that are equipped with counselors and psychologists who are trained to support students in need.
For students and those who have concerns, there are two things we can do at the very least to maintain mental health:
1. First and foremost, you must be able to acknowledge your thoughts and feelings.
We can’t control what’s coming to us, but we can control our response. As part of controlling our response, let’s accept our emotions, because all feelings (all emotions) are valid. Pain is a unique human experience. Don’t deny your feelings just because we don’t want to be called overly sensitive or ‘baper.’ We have the right to own it.
You may then select from a variety of responses that best suit your reaction. You have the option to avoid, modify, adapt, or simply accept the situation. In other words, allow yourself some space. Once you achieve mental clarity, your emotions will become more stable, enabling you to manage the circumstances more effectively.
2. Practice self-care, which means caring for yourself.
It includes anything we do to keep ourselves healthy — physically, mentally, and spiritually. It can be giving yourself a break that doesn’t cost anything, such as taking a walk, getting enough sleep, praying, reflecting, listening to audiobooks, meeting up with friends and family, and having a good laugh. Talking to someone, including a professional, is also part of self-care. Among so many things you can do, remind yourself to always be kind. You can be in pain but still be kind to others.
To conclude, everyone is struggling with their own mental health, including you and me. But we always have a choice to solve our problems. And we know, this too shall pass. Thus, keep embracing our values, be kind, and make space for ourselves.
One day we will say ... 'It was hard, but we made it.'
________________
*) A/Prof. Charyna Ayu Rizkyanti, Ph.D, is a mental health advocate and lecturer at the Faculty of Education, Universitas Islam Internasional Indonesia (UIII)
source: https://uiii.ac.id/perspectives/read/57695/happy-world-mental-health-day-from-uiii
Longitudinal Study of School Climate Instrument with Secondary School Students: Validity and Reliability Analysis with the Rasch Model

Zynuddin, S.N. & Sumintono, B. (2024).Longitudinal Study of School Climate Instrument with Secondary School Students: Validity and Reliability Analysis with the Rasch Model. Malaysian Online Journal of Educational Management, 12(4), 24-41. https://mojem.um.edu.my/index.php/MOJEM/article/view/55629
Abstract
The school climate plays a pivotal role in students’ outcomes. Previous literature has highlighted several methodological approaches employed in the school climate domain, including longitudinal studies. However, little is known about the validity and reliability of school climate instruments for longitudinal studies using Rasch analysis. Rasch model is a powerful approach to validate assessment on both item and test levels. Rasch model is coined from the probability of each response and includes item difficulty parameters to characterize the measured items. Moreover, the score represents the item and the person involved with the assessment. Thus, the current study aimed to validate school climate instruments for longitudinal studies with a six-month gap within the context of secondary school students by utilising Rasch analysis. This study evaluated aspects of reliability and validity, such as unidimensionality, rating scale analysis, item fit statistics, item targeting, and differential item functioning. A total of 1,495 secondary school students from public schools in Selangor, Malaysia, completed a 28-item Malay version of the school climate survey at Time-1 and Time-2, with a six-month gap. The results of the Rasch analysis indicated that the instrument had excellent reliability and separation indices, excellent unidimensionality and construct validity, a functional rating scale, good item-person targeting, and good item fit statistics. The current findings provided valid and reliable insights pertinent for policymakers to strategise interventions and initiatives to enhance the quality of school climate and overall education, particularly in the Asian context.
Lunch Talk #34: Critical Literacies, Gender and Social Inclusion

You are invited to join the Lunch Talk #34 at the Faculty of Education, UIII
Zulfa Sakhiyya, Ph.D. (Lecturer at Universitas Negeri Semarang and Scholar in Residence Batch 5, Faculty of Education, UIII) will share about: “Critical Literacies, Gender and Social Inclusion”.
This talk aims to examine the relationship between critical literacies and gender by exploring the literacy practices of feminist activists in Indonesia. In a relatively patriarchal culture, feminist activists in Dr Sakhiyya's study employ critical literacies to advocate gender equality and social inclusion in order to mobilize resources. From marching on the street to digital campaigns in social media, they have challenged the dominant discourse of functional literacy and women’s empowerment and demonstrated the adaptability of critical literacies in ongoing ways to support social activism and advocacy.
Day/Date: Tuesday/October 29, 2024
Time: 13.00-14.30 WIB
Place: Theater, Faculty A Building
Online participation:
https://bit.ly/LunchTalkEdu34
E-Certificate is provided
Thank you!
Recorded on YouTube
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=h-mPSVlKnuY
Garuda and Eagle: A Mexican Student’s Reflection on State Symbols at Indonesia’s Parliament
 Garuda and Eagle: A Mexican Student’s Reflection on State Symbols at Indonesia’s Parliament
Garuda and Eagle: A Mexican Student’s Reflection on State Symbols at Indonesia’s Parliament
October 06, 2024
Contributor: Supriyono | Editor: Dadi Darmadi | Photo: Achmad Jatnika
It was a bright morning on September 24, 2024, when 15 students from Universitas Islam Internasional Indonesia (UIII), led by the International Office and Student Affairs, boarded a bus for a special visit to the Indonesian Parliament Office and House of Representatives (DPR-MPR RI) in Central Jakarta. They were attending the OIC International Youth Summit, an event organized by OIC Youth Indonesia.
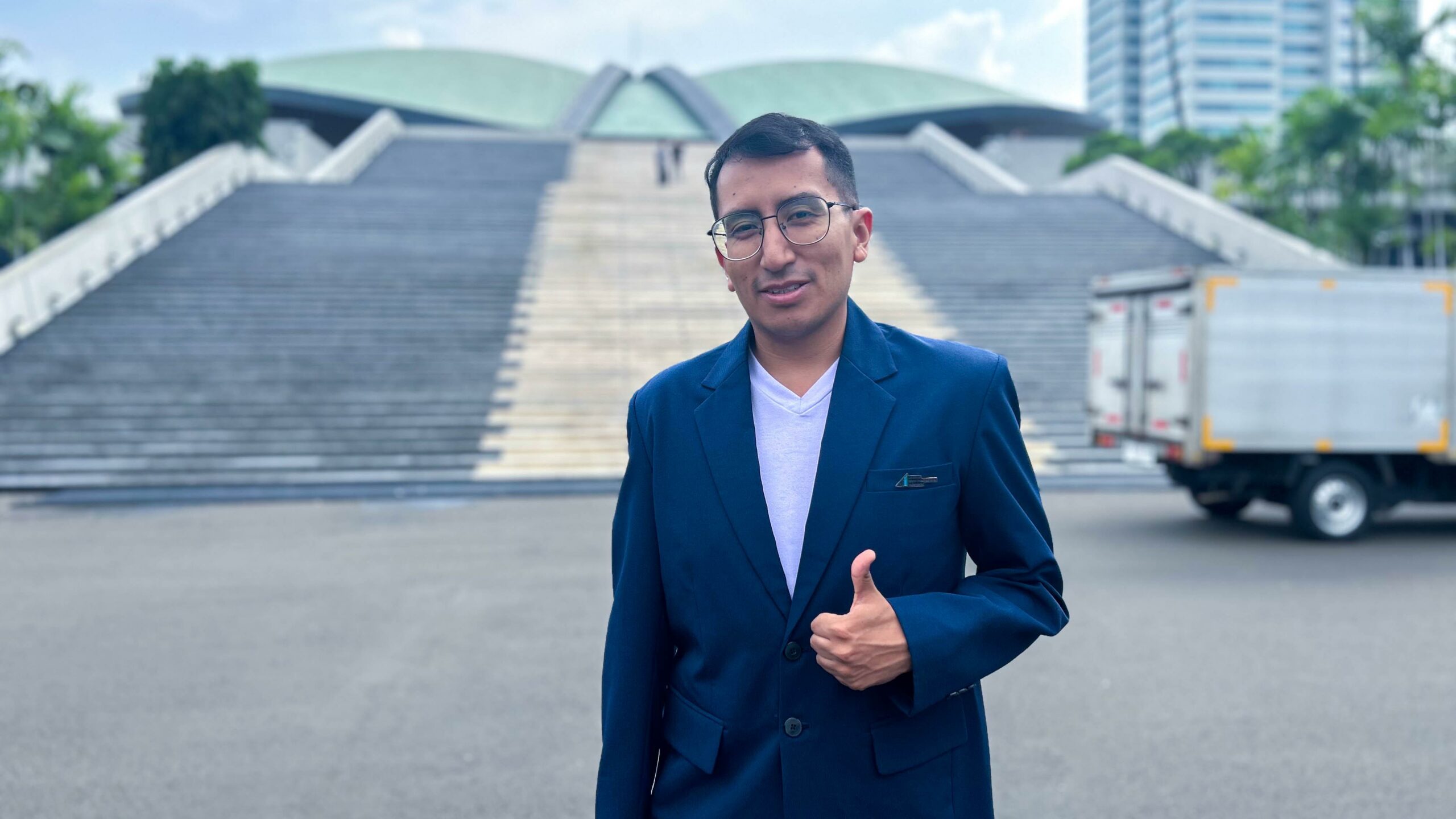
Among the students was Alberto Emmanuel Conti Morales, a PhD candidate from Mexico studying at UIII’s Faculty of Education. For him, this was not just an opportunity to engage in critical discussions but also a journey through culture and symbols that stirred deep reflections on identity and nationhood.
"The place is very nice, appealing, and interesting. I never thought we would be in such a formal and important setting. I had expected something more informal, so I was pleasantly surprised," he shared, marveling at the grandeur of the building, as they arrived at Gedung Nusantara V of the parliament office.
Having visited the Mexican Parliament ten years prior, Alberto found himself comparing the two structures. "In Mexico, the parliament building is bigger, but this one feels more modern. Perhaps it's because a decade has passed since my last visit. But what really caught my attention was the difference in the atmosphere, the Indonesian parliament seems to reflect a deep sense of national pride."
Alberto was especially captivated by the Indonesian national symbols. As he sat in the parliament, his eyes were drawn to the imposing Garuda emblem, a reminder of Indonesia’s foundational values.
"In Mexico, we have a national seal too, an eagle with a snake. It’s very similar to Indonesia’s Garuda in terms of strength and symbolism. But in Indonesia, the Garuda represents more than just a national identity. It embodies the spirit of Pancasila, the philosophical foundation of the country. I found that deeply fascinating because it highlighted how much meaning Indonesians place on their symbols,” he said.
The summit Alberto visited was an annual summit held by OIC Youth Indonesia, an organization aimed at empowering and uniting young Indonesians under the values of the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation (OIC). It provides a platform for youth engagement on both national and international levels, promoting collaboration, leadership, and dialogue.
As the summit began, the room filled with the voices of youth leaders and speakers, all discussing the role of young people in shaping a post-OIC world. The conversation quickly turned to the importance of religion in civil society—a topic that resonated deeply with Alberto. As someone who hails from a country where religion is increasingly seen as a personal matter, he was struck by the Indonesian emphasis on faith as a core element of national unity and progress.
"The discussion was interesting, especially because of how central religion is to society here in Indonesia. In Mexico, religion is no longer a public matter; it has become something personal, something private. But here, it's clear that religion still plays a significant role in nation-building. It was eye-opening to see how much Indonesians rely on their faith in shaping their civil society," Alberto reflected.
For Alberto, the OIC International Youth Summit was more than just a political event—it was a mirror reflecting the values of a nation, a reminder of the power of symbols and faith in shaping identity. As he left the Indonesian parliament office with his fellow students, he carried with him not only the lessons from the summit but also a deeper appreciation for the cultural richness of his host country, Indonesia.
Who says that men cannot take charge of early childhood education?

Who says that men cannot take charge of early childhood education?
October 03, 2024
Contributor: Intan Fasya Zahara & Queen Salsabila | Editor: Supriyono
For too long, the field of early childhood education has been stereotyped as a profession dominated by women. Many believe that nurturing young children, guiding their early learning, and working within early childhood development is best suited to women.
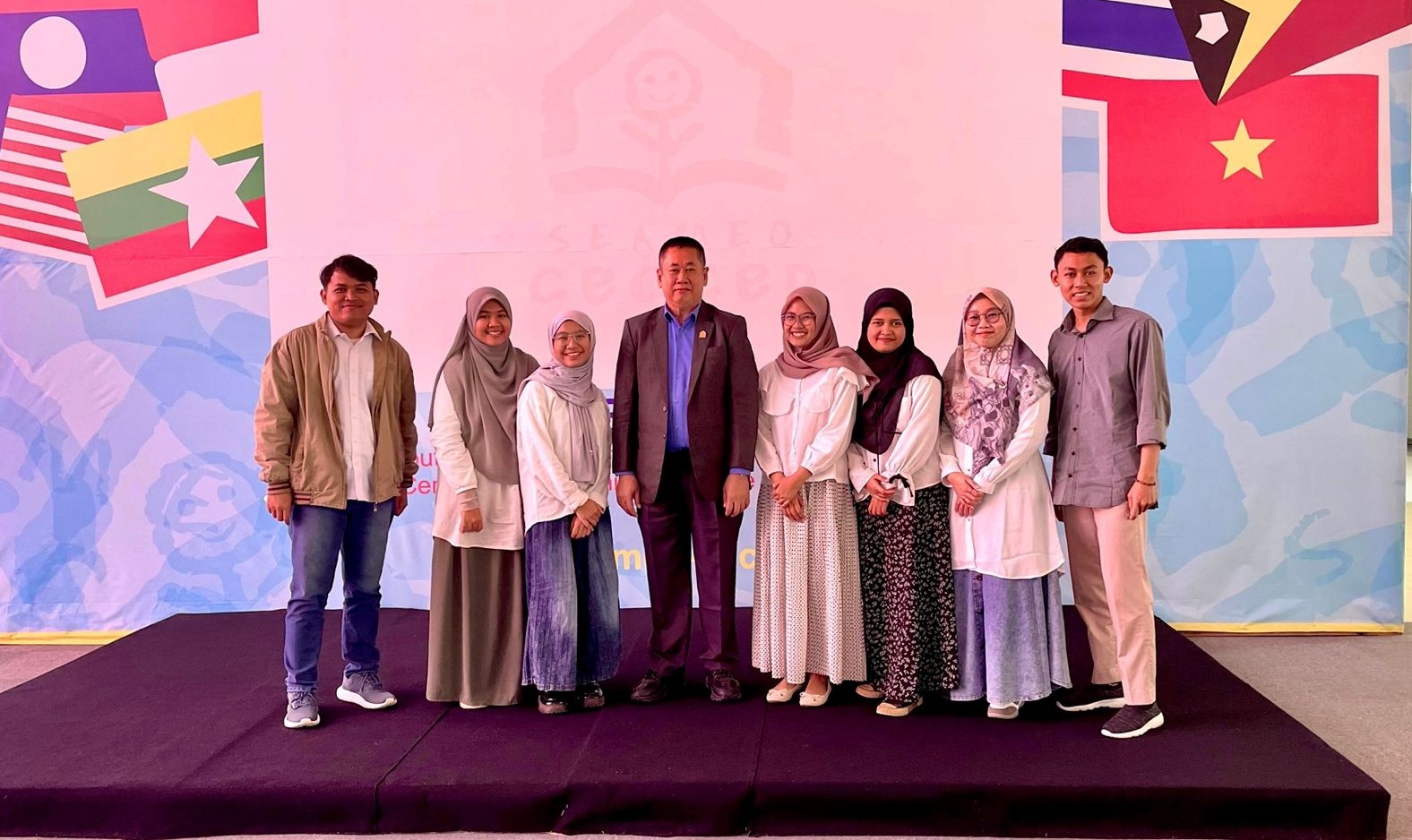
However, Muhamad Maulana and Muhammad Lutfi Assidiqi, two male students from the UIII Faculty of Education (FoE), set out to challenge this perception as they decided to intern at an organization focused on early childhood education across Southeast Asia in Bandung, West Java.
From July 22nd to August 22nd, 2024, Lutfi and Maulana, along with five other students from the faculty, participated in a month-long internship at SEAMEO CECCEP, a regional organization dedicated to early childhood care and education (ECCE) and parenting across Southeast Asia.
Lutfi, who was assigned to the Advocacy and Partnership division, found the experience particularly enriching. "I was initially nervous about how I’d be received as a male in this field, but I quickly realized that my gender didn’t matter. What mattered was my contribution to the discussions and projects,” he reflected.
Lutfi's tasks were varied and challenging. He participated in policy discussions, worked on a curriculum for Cambodia, and helped prepare reports that would later be launched internationally. “Being involved in these projects helped me see that men, too, have an important role in shaping the future of early childhood education,” he added.
Similarly, Maulana, who worked in the Research and Development (RnD) division, shared his experience of facing societal assumptions. “I’m particularly aware that the field of early childhood is often associated with women,” he said. "But during the internship, I realized how much value men can bring to this field.”
Maulana’s role involved working on parenting and the child’s transition from kindergarten to elementary school. He was particularly mesmerized by how early childhood education shapes individuals’ lives into adulthood. “We’re not just dealing with children; we’re building the foundation for future generations,” he noted.
This internship experience has allowed Lutfi and Maulana to shatter preconceived notions about men in early childhood education. Their participation not only challenged societal stereotypes but also opened doors for future male students to be involved in the field. Their spirit aligns closely with the values that UIII upholds in promoting gender equality in education, particularly in early childhood.
This internship is a component of the Independent Study course offered by the Faculty of Education, allowing students to engage in self-directed projects that contribute to their future career or research growth. In addition to partnering with organizations like SEAMEO CECCEP, students have also gained internship experience at the Indonesian House of Representatives (DPR RI) and various international schools in Indonesia.